A Comprehensive Guide to Protective Put
What is a Protective Put?
This can be thought of as an insurance policy. This is commonly deployed when you own the underlying asset but feel the price may go down and wish to protect your position in an event of a downturn or uncertainty. The main goal is to limit potential losses from an existing position. This is also known as a synthetic long call as once in place its risk/reward is the same as a long call. If the stock and the put are bought at the same time, this can be referred to as a married put but essentially works the same.
If you buy a protective put, you have control over whether to exercise your option or not at the strike price you chose.
Adopting such a strategy does not cap your potential profits. The profits from the strategy are determined by the growth potential of the underlying asset itself. However, a portion of the profits is reduced by the premium paid for the put option.
This strategy will create a limit for potential losses as any losses in the stock position below the strike of the put option will be compensated by profits in the option.
When you Might Consider Buying a Protective Put
- Risk Management: One of the primary reasons to use a this strategy is to manage risk. Investors can limit their potential losses if the price of the underlying asset drops. This can be particularly useful if an investor has a significant position in the underlying asset and wants to protect themselves against a sudden decline in value.
- Hedging: Investors may also use the strategy to hedge their existing positions. For example, if an investor owns a stock and is concerned about a potential market downturn, they can buy a protective put option on that stock to limit their potential losses.
- Speculation: Some investors may use this as a speculative strategy. For example, if an investor believes that the price of the underlying asset will increase significantly but is concerned about potential short-term volatility, they can purchase a protective put option to protect against any potential losses in the short term.
- Peace of Mind: For risk-averse investors, a protective put can provide peace of mind knowing that they have a safety net in case the price of the underlying asset drops. This can reduce the psychological stress of investing in volatile markets and help investors stay disciplined in their investment strategies.
- Diversification: By using this strategy, investors can diversify their portfolios by adding an option component that can help reduce risk and provide a more balanced risk-return profile.
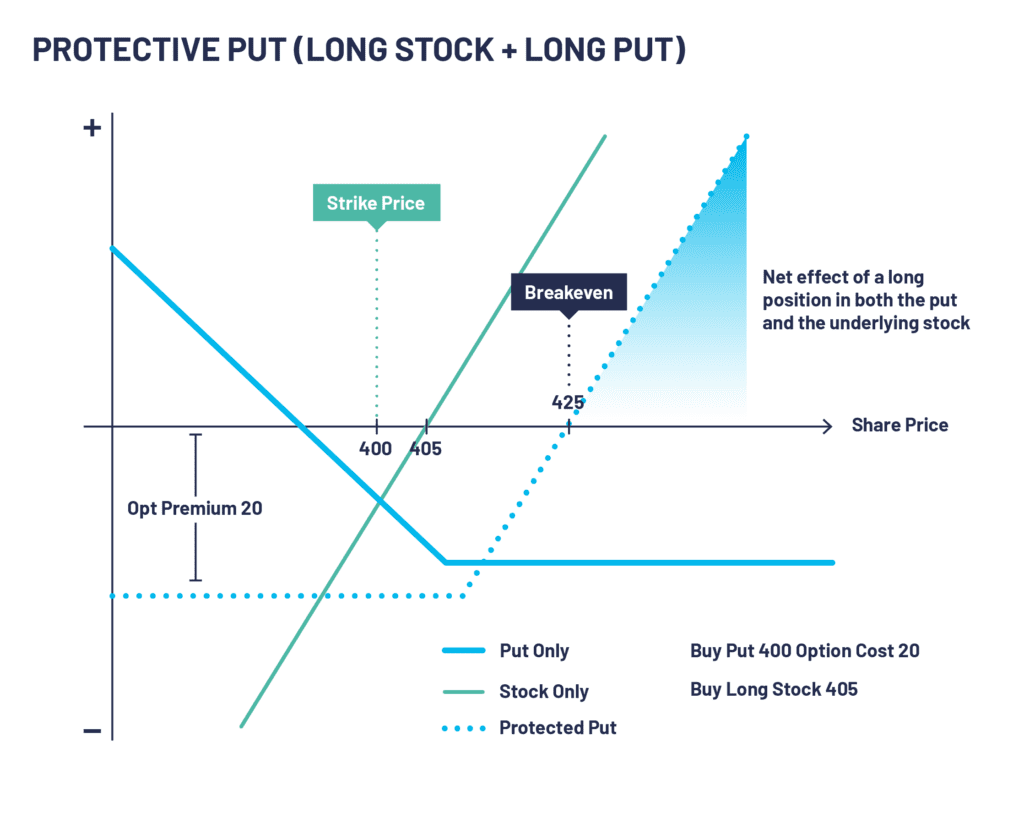
PROTECTIVE PUT SCENARIO AND EXAMPLE
For this example, we will say you own shares of XYZ PLC, with each share valued at 405.
You feel that the value of these shares may fall in the short term, but you want to keep ownership of them for several potential reasons (e.g., they pay a good dividend; you don’t want to crystallise a capital gain; they are a good long-term hold).
Therefore, instead of selling the shares you buy a protective put to hedge against the risk of a decline in their price, with a strike price of 400. The premium is 20.
SHARE PRICE RISES ABOVE 425
- If the share price goes beyond 425, you will experience a gain in the overall position as your breakeven point was the stock price paid plus the premium paid for the option
SHARE PRICE BETWEEN 400 AND 425
- In this scenario, the share price will remain the same or slightly rise. However, you will lose money in the form of the premium you paid for the protective put option itself
SHARE PRICE BELOW 400
- In this scenario, you have the right, but not the obligation to exercise the protective put option to limit the losses. Once the put is exercised, you will sell your shares at 400. Thus, your loss will be limited to 25 as your net selling price will be 380 (400 -20 option premium)
Advantages of Using a Protective Put:
- Protection against downside risk: By buying a protective put option, an investor can limit their potential losses if the price of the underlying asset falls.
- Flexibility: The strategy is flexible because the investor can choose the strike price and expiration date of the put option based on their individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Potential for profit: If the price of the underlying asset increases, the investor can still profit from the increase in value while having the peace of mind that their downside risk is limited.
Risks of a Protective Put:
- Cost: Buying a protective put option involves paying a premium, which can reduce the investor’s overall return on investment.
- Reduced profit potential: While the protective put strategy limits downside risk, a portion of the profits will be reduced by the premium paid for the put option.
How Does Volatility Impact a Protective Put?
Volatility can have a significant impact on a protective put strategy. Volatility is a measure of the magnitude of price movements in the underlying asset, and it can affect the price of options contracts, including protective puts.
If the volatility of the underlying asset increases, the price of the protective put option may also increase. This is because the higher volatility makes the option more valuable as it provides a greater chance that the underlying asset will drop in price. Therefore, the cost of buying a protective put option may be higher during times of high volatility, which can reduce the overall return on investment.
On the other hand, if the volatility of the underlying asset decreases, the price of the protective put option may decrease as well. This is because the lower volatility makes the option less valuable as it reduces the likelihood of the underlying asset’s price falling below the strike price of the put option. In such situations, the cost of buying a protective put option may be lower, which can increase the overall return on investment.
Does Time Decay Have an Effect on a Protective Put?
Time decay, also known as theta, can also have an impact on the effectiveness of the strategy. Time decay refers to the fact that the value of an options contract, including a protective put, decreases as time passes and the expiration date of the option approaches.
As the expiration date of a protective put option approaches, the time decay accelerates, causing the value of the option to decrease more rapidly. This means that the value of the protective put as a form of insurance against price drops in the underlying asset will decrease over time.
Therefore, if an investor buys a protective put option and holds it for an extended period, the cost of the option may decrease due to time decay, which could reduce the effectiveness of the protective put as a form of risk management.
To counteract the effects of time decay, investors can consider purchasing protective put options with longer expiration dates. The longer the expiration date of the put option, the slower the time decay and the more time the investor must benefit from the protective put strategy.
It’s important to note that while a longer expiration date can reduce the impact of time decay, it may also increase the cost of the protective put option. Therefore, investors should carefully consider the balance between the cost of the protective put option and the length of the expiration date to effectively manage risk and maximise potential returns.
How is the Strike Price of a Protective Put Determined?
The strike price of a protective put is determined based on the investor’s desired level of protection and their investment goals. The strike price is the price at which the investor has the right to sell the underlying asset in case of a price drop.
In general, the strike price of a protective put is set below the current market price of the underlying asset. The idea is that if the price of the underlying asset drops below the strike price, the investor can exercise their right to sell the underlying asset at the higher strike price, thereby limiting their losses.
PROTECTIVE PUT SUMMARY
CONFIGURATION:
- If the underlying asset is currently owned
- Buy a put with a strike price near the underlying asset’s current market price
OUTLOOK:
- Longer term bullish but uncertain of the future
TARGET:
- Stock to rise and your option to expire worthless. You can enjoy the profits on your stock position
Protective Put FAQs
What is a protective put in options trading?
A protective put is an options trading strategy in which an investor buys a put option to protect their stock holdings against a potential drop in price.
How does a protective put work?
When an investor buys a protective put, they have the right to sell their shares at a specific price (the strike price) until the expiration date of the option. If the price of the underlying asset drops, the investor can exercise their put option and sell their shares at the strike price, protecting them from further losses.
What is the cost of a protective put?
The cost of a protective put is the premium paid for the option. This premium is the price an investor pays for the right to sell their shares at the strike price, and it varies depending on factors such as the stock price, strike price, and expiration date.
Is a protective put right for me?
Investors who hold a significant amount of stock and are concerned about a potential drop in price may consider using a protective put strategy to limit their downside risk.
What are the advantages of a protective put strategy?
The potential benefits of a protective put strategy include limiting downside risk, providing a form of insurance against a potential drop in stock price, and allowing investors to continue to hold their stock while protecting their position.
What are the risks of a protective put strategy?
The potential drawbacks of a protective put strategy include the cost of the premium paid for the option, the potential for the stock price to increase and the put option to expire worthless, and the possibility of over-insuring a position and reducing potential gains.
How do I determine the strike price and expiration date for a protective put option?
The strike price and expiration date for a protective put option should be based on an investor’s risk tolerance, the amount of stock they hold, and their investment goals. It is recommended to consult with a financial advisor or options trading professional to determine the appropriate strategy for your individual needs.
Can I use a protective put with other options trading strategies?
Yes, a protective put can be used in combination with other options trading strategies, such as a covered call, to create more complex hedging strategies that can offer even greater protection against downside risk. However, it is important to understand the risks and potential rewards of each strategy before implementing them in your portfolio.


