The Short Straddle: How to deploy this Option Trading Strategy
What is a Short Straddle?
Options straddles can be split into two different configurations, a Long Straddle and a Short Straddle. We’re going to run through the short straddle to explain what you will need if you wanted to run this strategy.
The Fundamentals of Short Straddle Strategy
A short straddle strategy involves selling a call and a put option simultaneously with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is particularly viable when you predict low/declining volatility in the underlying asset’s price or expect to the share price to remain relatively stable.
This strategy allows you to profit from a market that is essentially moving sideways. With this strategy you collect two premiums from the sale of the call and put upfront, but the trader builds a larger margin of error compared to writing just a call or a put option individually. However, the risks are substantial on the downside and unlimited on the upside, should a large move occur.
Short Straddle Mechanics: Breaking Down the Steps
In executing a short straddle, the steps are surprisingly straightforward, given its reputation as an advanced strategy. Below is a simple breakdown:
Identify the Underlying Asset
Choose an asset that you believe will exhibit low volatility in the short to medium term.
Sell a Call Option
This involves selling a call option on the chosen asset with a specific strike price.
Sell a Put Option
Simultaneously, sell a put option on the same asset, with the identical strike price and expiry date.
A short straddle is a strategy where you write (sell) calls and write (sell) puts, both with the same strike price and expiration. As you can see by the payoff diagram, it is the complete opposite of the long straddle. Together, the options produce a position that hopes for a stagnant marketplace with low volatility.
This strategy allows you to profit from a market that is essentially moving sideways. With this strategy you collect two premiums from the sale of the call and put upfront, the investor builds a larger margin of error, compared to writing just a call or a put option individually. However, the risks are substantial on the downside and unlimited on the upside, should a large move occur.
Analysing Potential Outcomes of the Short Straddle Strategy
When correctly implemented, a short straddle can yield good returns. However, the results can vary, contingent on the movement of the underlying asset.
Scenario 1: Underlying Asset Price Stays Stable
Should the asset’s price remain at the strike price by the time of expiration, both the call and put options will expire worthless. As the seller, you retain the entire premium received from selling both options.
Scenario 2: Underlying Asset Price Moves Significantly
If the price veers too far from the strike price, either upward or downward, potential losses could be significant. The danger lies in the unlimited risk to the upside (if the price of the asset rises) or the risk to the downside (if the price falls below the strike price minus the collected premium).
Managing Risks in a Short Straddle
While the short straddle’s potential returns are appealing, the risk involved cannot be underestimated. However, adopting suitable risk management practices can help mitigate potential losses.
Close Positions Early: If the price of the underlying asset begins to move significantly, consider closing out the position early to prevent further losses.
Adjust the Straddle: Adjusting the strike prices of the call and put options can help manage losses in the event of large price swings.
The Market Conditions Suitable for a Short straddle
The success of the short straddle largely depends on the market conditions. The ideal scenario for employing this strategy is when the market is showing signs of low volatility. This means the prices of the underlying assets are expected to remain stable or fluctuate within a narrow range.
Crafting a Short Straddle: Selecting the Strike Price
The strike price is a critical determinant in the profitability of the short straddle. The ideal strike price is at the money, meaning it’s equivalent to the current market price of the underlying asset. This selection is predicated on the expectation that the asset’s price will remain relatively static.
The Art of Timing: Deciding the Expiration Date
The expiry date is another pivotal factor in the short straddle. As a rule of thumb, options with shorter expiration dates are preferable because the likelihood of significant price movement in a short period is generally lower than in a longer one.
The Role of Implied Volatility in the Short Straddle
Implied Volatility (IV) plays an essential role in the success of a short straddle. High IV, which signifies greater price fluctuation, can result in substantial premiums for the option seller. However, it increases the risk of price movement, potentially leading to losses. Therefore, it’s a careful balance that needs to be struck.
Short Straddle Example
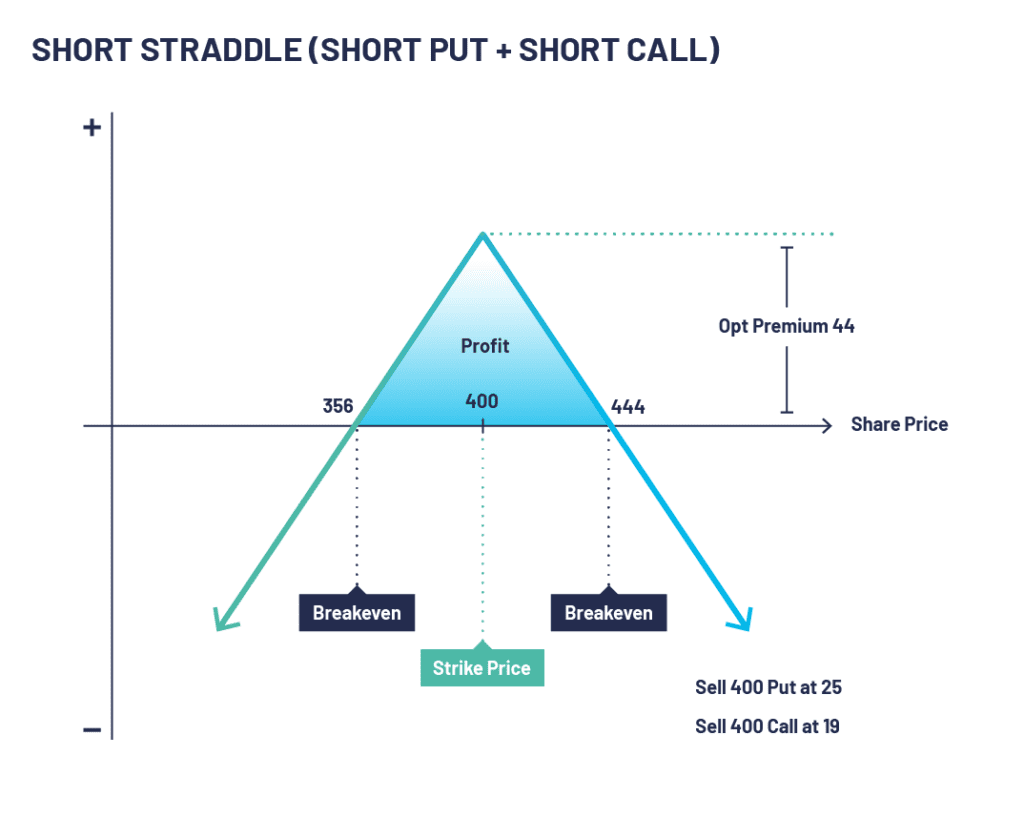
Let’s look at an example of a short straddle. XYZ PLC stock is trading at 395. An options trader executes a short straddle by selling a 400 put at 25 and a 400 call at 19. The net credit taken to enter the trade is the maximum possible profit (44).
If XYZ PLC stock rises and is trading at say 500 on expiry, the 400 puts will expire worthless but the 400 calls expire in-the-money and have an intrinsic value of 100 thus creating a loss of 56 (100-44) The same will happen if, for example, the stock was trading at 300 but with the 400 puts having an intrinsic value of 100.
On expiration, if XYZ stock is trading close to 400, both the 400 put and the 400 call could be bought back for maybe 2 or 3 creating a profit of around 40.
Short Straddle Summary
The short straddle can be a rewarding strategy when effectively employed. The allure of high returns in a non-volatile market can be enticing to traders. However, this comes with a higher degree of risk and requires diligent market analysis and precise execution. It’s a dual-edged sword that can yield significant profits when wielded correctly. As with all trading strategies, mastering the short straddle requires practice, patience, and a keen understanding of the market’s many nuances.
Configuration:
- Sell a put with a strike price typically at the money
- Sell a call with the same strike price as the put and with the same expiry
Outlook:
- Anticipates decreased volatility – You think a period of calm is coming and have a neutral view
Target:
- Underlying price of the asset to not move away from the strike you have chosen
Pros:
- Premiums can be very attractive
- High time decay in a neutral market
Cons:
- Higher risk strategy
- Beware of high margins
- Potential losses can accumulate very quickly
- Assignment risks on both options if they are American style


