Bear call spread
What is a Bear Call Spread?
A Bear Call Spread is an options trading strategy employed when an investor anticipates a modest decrease in the price of an underlying asset. It consists of selling a call option with a lower strike price (in-the-money) and buying another call option with a higher strike price (out-of-the-money) on the same underlying asset with the same expiration date. By executing this strategy, the investor can generate premium income, which is maximised if the underlying asset’s price stays below the lower strike price at expiration.
This is a bearish strategy that benefits from the protection of capping your maximum loss with the trade-off being you have to pay for this protection.
The maximum profit potential of the trade is the net credit received. The maximum loss potential of the trade is easily calculated. Simply take the difference between strike prices and add the net premium received for the call spread.
When would you use this strategy?
If you think the market will fall but want protection just in case your assumption is incorrect and you want to cap your potential losses. If you don’t own the underlying stock it’s prudent to sell call spreads, because the loss potential is unlimited for naked short calls.
Here are a few scenarios where it can prove beneficial:
Hedging against downside risk
If an investor owns an asset and fears a modest decrease in its value, a Bear Call Spread can help hedge against this downside risk while generating income through collected premiums.
Neutral market conditions
If the market is expected to move sideways, investors can use this strategy to generate income from the premiums, assuming the underlying asset’s price remains below the lower strike price.
Taking advantage of high volatility
High implied volatility can inflate option premiums. In such a scenario, the Bear Call Spread can be an effective strategy to harvest higher premiums while managing risk with the purchased call.
Mechanics of the Bear Call Spread
Establishing the Spread
To establish a Bear Call Spread, an investor sells an in-the-money call option (lower strike price) and simultaneously purchases an out-of-the-money call option (higher strike price) on the same underlying asset, with both options sharing the same expiration date.
The collected premium from selling the lower strike price call helps offset the cost of buying the higher strike price call, thus reducing the overall investment cost. The maximum possible profit is the net premium received, which occurs if the price of the underlying asset remains below the lower strike price at expiration.
Managing the Risk
While this strategy is a common tool to hedge against potential losses, it’s not without risk. The potential loss from a Bear Call Spread is limited to the difference between the two strike prices, minus the net premium received. This loss occurs if the price of the underlying asset rises above the higher strike price at expiration.
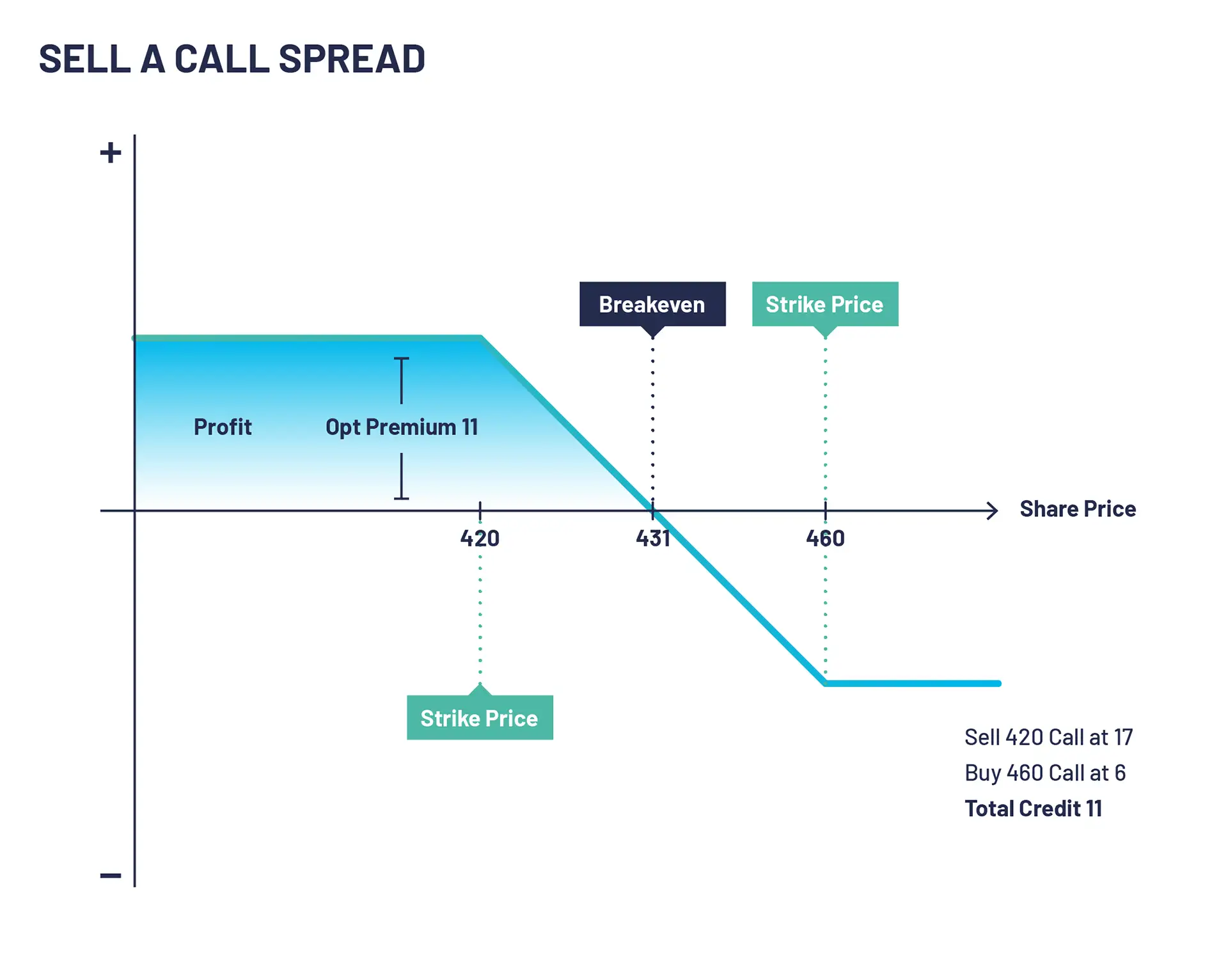
Bear Call Spread Example
Let’s look at selling a call spread example. XYZ is trading at 412. An options trader executes selling a call spread by selling a 420 call at 17 and buying a 460 call at 6. The net credit received and maximum profit on this trade is 11 (17-6).
If XYZ is trading below 420 on expiry the maximum profit is realised as both calls expire worthless and you keep the premium received. If XYZ PLC stock rises and is trading above 460 on expiry the maximum loss on this trade is realised. At expiry, you would be exercised on the 420 calls selling the shares for 420 while simultaneously buying the shares at 460 with the exercise of the 460 call locking in a 40 loss minus the credit received.
Bear Call Spread Summary
A Bear Call Spread can be a powerful tool in an investor’s arsenal, particularly when expecting minor bearish movements or stagnant prices. While its income-generation and risk-management attributes make it an attractive strategy, it’s crucial to understand the risks involved and necessary considerations for implementation. Ultimately, a well-executed Bear Call Spread can help investors navigate uncertain markets and extract value from their investment decisions.
Configuration:
- Sell a call option
- Buy a call option with a higher strike and the same expiry date.
Outlook:
- Anticipate a moderately bearish move
Target:
- Underlying stock price expires below the strike of the sold call option
Pros:
- Defined risk strategy.
- Takes advantage of time decay as both options near expiry, the value of the spread becomes cheaper to buyback.
- Lower margin requirement compared to selling naked calls.
Cons:
- Can be exercised early if American style.
- Limited profit potential.
- Can be margin intensive if the underlying asset rises sharply.
Bear Call Spread FAQs
What is a Bear Call Spread in options trading?
A Bear Call Spread is an options trading strategy that involves selling a call option with a lower strike price and buying another call option with a higher strike price, both on the same underlying asset and with the same expiration date. It’s used when an investor expects a modest decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
When should an investor use the Bear Call Spread strategy?
A Bear Call Spread is typically used when an investor has a neutral to slightly bearish outlook on the market. It can be an effective strategy to generate income during stagnant market conditions, or as a hedge against slight decreases in an owned asset’s value.
What are the risks involved in a Bear Call Spread?
The potential risk in a Bear Call Spread is limited to the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium received. This maximum loss occurs if the underlying asset’s price exceeds the higher strike price at expiration.
What factors should be considered when establishing a Bear Call Spread?
Key factors include the choice of strike prices, the expiration date of the options, the implied volatility of the underlying asset, and having a clear exit strategy.
How does implied volatility affect a Bear Call Spread?
High implied volatility can lead to higher option premiums. Thus, if an investor’s outlook on the underlying asset’s price is correct, a Bear Call Spread can be more profitable during periods of high volatility.
What is the maximum profit in a Bear Call Spread?
The maximum profit in a Bear Call Spread is the net premium received from selling and buying the call options. This profit is realized if the underlying asset’s price stays below the lower strike price at expiration.
How can an investor limit their losses with a Bear Call Spread?
The purchased call option in a Bear Call Spread acts as a hedge against significant upward price movements, thereby limiting the potential loss to the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium received.
How does the choice of strike prices impact a Bear Call Spread?
The width of the spread (difference between strike prices) directly impacts the potential profit and risk. A wider spread can offer higher profits but also involves greater risk.
What role does the expiration date play in a Bear Call Spread?
The expiration date can affect the premiums of the options. Options with longer expiry dates usually command higher premiums due to increased uncertainty over time.
Can a Bear Call Spread be used for bullish markets?
No, a Bear Call Spread is typically not suited for bullish markets. If an investor expects the underlying asset’s price to rise, other strategies like the Bull Call Spread would be more appropriate.
Check out our other articles