Understanding the Bear Put Spread
What is a Bear Put Spread?
A bear put spread is a vertical options strategy that consists of buying and selling put options on the same underlying security with the same expiration date, but at different strike prices. This strategy allows investors to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset while limiting their potential loss. Here is a step-by-step description of the bear put spread:
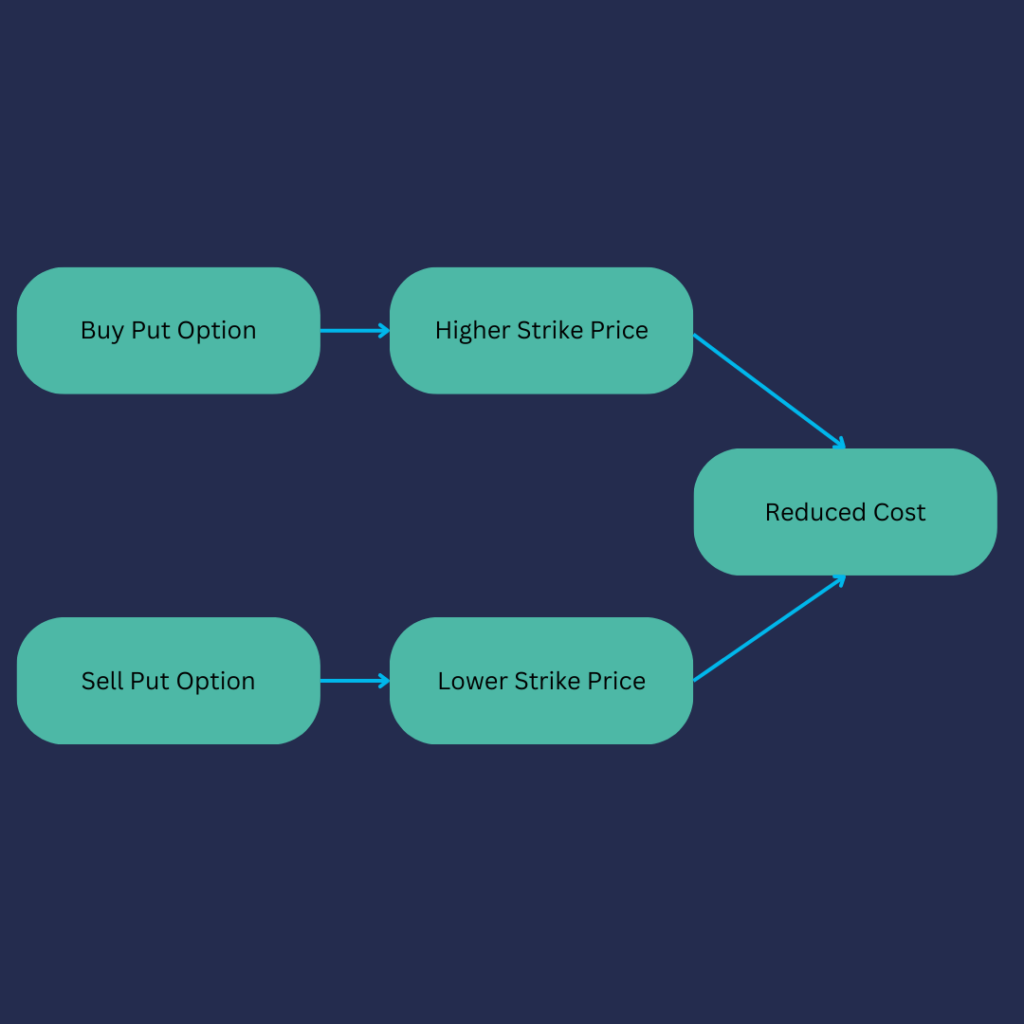
- Buy a put option: Purchase a put option with a strike price that is slightly above the current market price of the underlying asset.
- Sell a put option: Simultaneously, sell a put option with a lower strike price than the purchased put option.
By selling the lower strike put option, the investor partially offsets the cost of buying the higher strike put option, thus reducing the overall cost of the trade.
Advantages of the Bear Put Spread
The bear put spread offers several benefits for investors:
- Limited risk: The maximum loss is capped at the net premium paid for the options, minimising the potential downside.
- Moderate profit potential: Although not as high as other more aggressive strategies, the bear put spread offers a reasonable profit potential.
- Cost-effective: By selling a put option, investors can lower the overall cost of the trade compared to buying a single put option outright.
Risks and Limitations
While the bear put spread offers attractive benefits, it is essential to understand its risks and limitations:
- Limited profit potential: The maximum profit is limited to the difference between the strike prices, minus the net premium paid.
- Less flexibility: Although the position can be closed out at any time, investors must wait until the expiration date if they want to realise the full potential of the strategy, which may not be ideal for active traders.
Does Volatility Affect a Bear Put Spread?
The impact of volatility on a bear put spread is relatively minimal. This is because a bear put spread consists of both a long put and a short put, resulting in a near-zero vega.
Vega, which measures how an option price changes in response to volatility adjustments while other factors remain constant, has limited influence on the price of a bear put spread. Consequently, changes in volatility have little effect on the overall value of the strategy, distinguishing it from other option strategies that exhibit more substantial vega.
While volatility remains an essential factor in option pricing, its impact on bear put spreads is relatively subdued, allowing investors to focus on other crucial aspects when implementing this strategy.
How Does Time Affect a Bear Put Spread?
Time plays a significant role in a bear put spread strategy. As time passes, the value of options tends to decline due to the diminishing time value component. In a bear put spread, the objective is for the stock price to decrease, resulting in an increase in the value of the long put option.
However, as time progresses, the value of both the long put and the short put options will erode. The long put option, which provides downside protection, will experience a decline in value due to the passage of time. Conversely, the short put option, which is sold to offset the cost of the long put, benefits from time decay as its value diminishes.
The impact of time decay can be both advantageous and disadvantageous for a bear put spread strategy. If the stock price remains above the strike price of the short put option, time decay can work in favour of the trader by reducing the overall cost of the spread. However, if the stock price declines significantly and falls below the strike price of the purchased put option, the effect of time decay on the long put option may reduce the overall profit potential.
Trading A Bear Put Spread
- Select the underlying asset: Identify the security that you believe will experience a moderate price decline.
- Choose the expiration date: Select an expiration date that provides enough time for the anticipated price movement to occur.
- Determine the strike prices: Choose a higher strike price for the purchased put option and a lower strike price for the sold put option.
- Calculate the net premium: Subtract the premium received from selling the lower strike put option from the premium paid for the higher strike put option.
- Monitor the trade: Keep an eye on the underlying asset’s price movement and be prepared to close the position if necessary.
Closing the Position
There are two primary ways to close a bear put spread:
- Letting the options expire: If both options are in-the-money at expiration, they will be automatically exercised, and the investor will realise the maximum profit. If both options are out-of-the-money, they will expire worthless, resulting in a loss limited to the net premium paid.
- Closing the trade before expiration: If the price movement is favourable before the expiration date, the investor can choose to close the position early by selling the higher strike put option and buying back the lower strike put option. This allows the investor to lock in profits without waiting for the options to expire.
Bear Put Spread Example
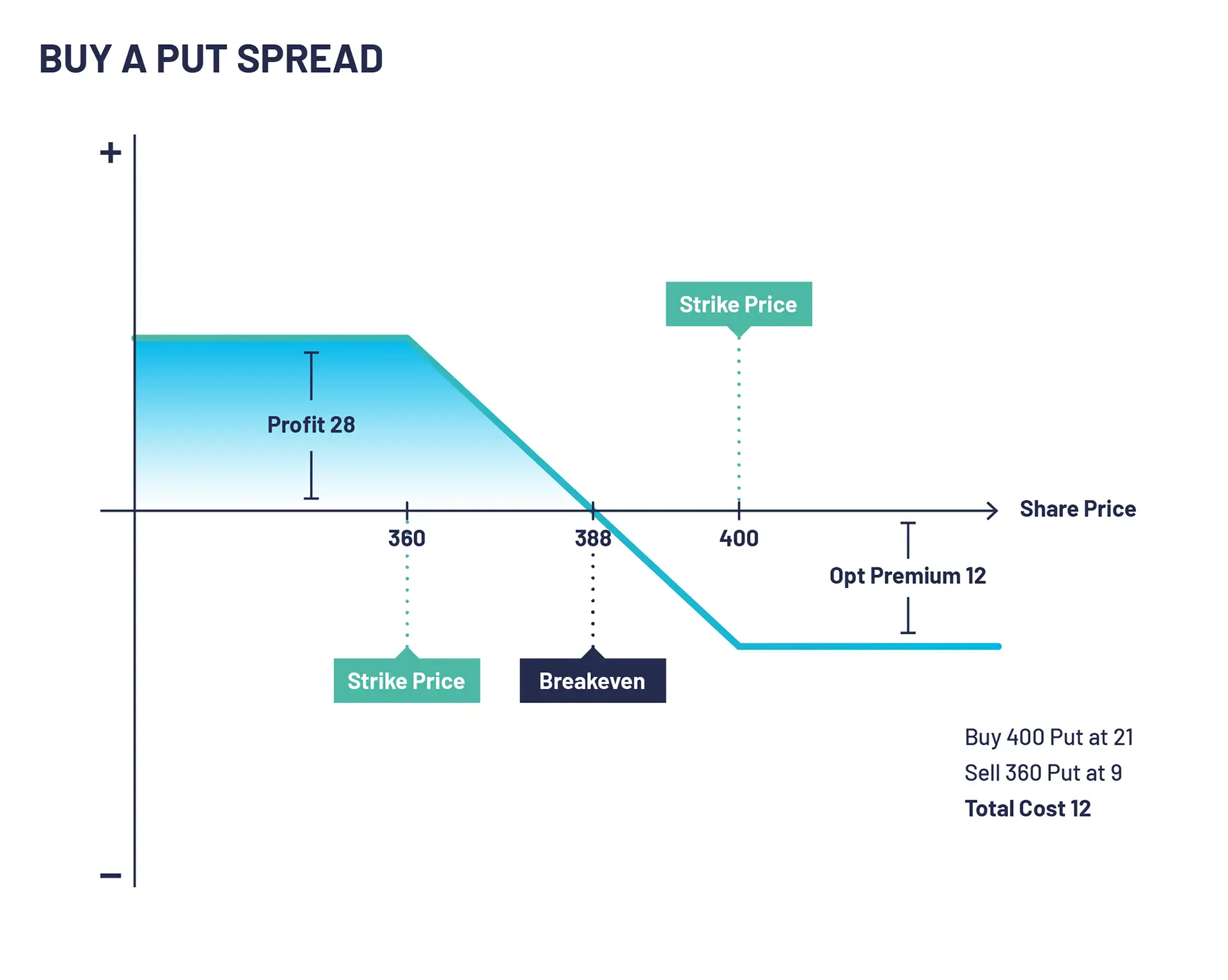
Let’s look at a bear put spread example. XYZ is trading at 412. An options trader executes buying a put spread by buying a 400 put at 21 and selling a 360 put at 9. The net debit and maximum loss on this trade is 12 (21-9).
If XYZ PLC stock falls and is trading below 360 on expiry of the options the maximum profit on this trade is realised. Technically the short 360 and long 400 puts would be exercised simultaneously, resulting in you purchasing the shares for 360 while simultaneously selling the shares at 400. In practise you would normally sell your put spread for close to 40 being the difference between the two strike prices.
If the stock closes above 400 both options expire worthless and the initial debit paid is lost.
Bear Put Spread Summary
A bear put spread is an options trading strategy that involves buying a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a put option with a lower strike price on the same underlying stock. The purpose of this strategy is to profit from a decline in the stock price. The long put option provides downside protection, while the short put option helps offset the cost of the long put. The maximum profit is achieved if the stock price drops below the strike price of the purchased put option, while the maximum loss is limited to the initial cost of establishing the spread.
Bear Put Spread FAQs
What is a bear put spread?
A bear put spread is an options trading strategy that involves buying a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously selling a put option with a lower strike price on the same underlying stock. It is used to profit from a potential decline in the stock price.
What is the purpose of a bear put spread?
The purpose of a bear put spread is twofold. First, it provides downside protection by limiting potential losses if the stock price rises. Second, it helps offset the cost of the long put option by selling a lower strike put option.
How does a bear put spread make a profit?
A bear put spread generates a profit if the stock price decreases. The maximum profit is achieved when the stock price drops below the strike price of the purchased put option. The profit is calculated as the difference between the strike prices minus the initial cost of establishing the spread.
What is the maximum loss in a bear put spread?
The maximum loss in a bear put spread is limited to the initial cost of setting up the spread. This occurs if the stock price remains above the strike price of the purchased put option at expiration.
What factors should be considered when selecting strike prices for a bear put spread?
When choosing strike prices for a bear put spread, it is important to consider the desired level of downside protection and potential profitability. The strike price of the purchased put option should reflect the expected decline in the stock price, while the strike price of the sold put option should help offset the cost of the strategy.
How does time decay impact a bear put spread?
Time decay, or the erosion of option values over time, affects a bear put spread. As time passes, the value of both the long put and short put options will decline. Traders need to be mindful of time decay and consider the remaining time until expiration when managing their positions.
What is the breakeven point in a bear put spread?
The breakeven point in a bear put spread is the stock price at which the strategy neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. It can be calculated by subtracting the net cost of the spread from the strike price of the purchased put option.
Can a bear put spread be adjusted or closed before expiration?
Yes, a bear put spread can be adjusted or closed before expiration. Traders may choose to close the spread early to lock in profits or limit losses. Adjustments can be made by rolling the spread to a different set of strike prices or closing out one leg of the spread while leaving the other leg open.
Are there any risks associated with a bear put spread?
While a bear put spread offers downside protection, there are still risks involved. If the stock price remains above the strike price of the purchased put option, the maximum loss is limited to the initial cost of establishing the spread. Additionally, factors such as changes in volatility or unexpected market events can impact the overall profitability of the strategy. Traders should carefully assess and manage these risks.
Check out our other articles


